
Want a Smart home/building that has it all?
KNX IoT devices and solutions evolve smart
homes and buildings to the next level.
Why KNX IoT?
- Interoperable & secure: KNX has been the reference when talking about interoperability. Just grab any two certified devices from any vendor, and they will simply work together at the application level in a secure way. Following this philosophy, KNX IoT has been designed to maintain the highest level of security. KNX IoT devices come with security embedded by design. With this robust new KNX IoT technology, manufacturers and developers can build the best devices, solutions, and services that will be installed by professionals of the industry of smart homes and buildings.
- Native KNX IoT Devices (IPv6): KNX devices now use a new approach to fit into the IPv6 architecture. The new generation of KNX IoT devices will be able to connect to IP networks (wired and/or wirelessly) to have communication with other KNX IoT devices as well as with KNX classic devices that use Twister Pair or Radio Frequency.
- Standardized API: For Those devices that need to be integrated into a KNX network, it is now possible thanks to a standardized API that can connect with KNX installations. This API is simple, secure, abstracted from the KNX-specific knowledge and future proof.
- One Tool: ETS: All of these capabilities are made possible through the use of ETS. With ETS, KNX devices from over 500 manufacturers can be configured independently of their physical layer, and project information can be exported to any KNX IoT API Server using a vendor independent tool. ETS provides core interoperability in an attractive tool with a modern user interface.
- KNX, the largest ecosystem in home and building automation: With this new possibility to communicate using the KNX Technology, it brings more flexibility. Manufacturers can now use new development possibilities to create innovative products and solutions; as well as professionals have more possibilities to create a bigger KNX ecosystem in their projects.
Make any home and building Smart with KNX IoT
Learn why KNX IoT opens up a world of possiblity for smart homes and buildings in this short introduction video.
You can find more detailed videos and webinars on KNX IoT our YouTube channel.
KNX, the largest development landscape of its kind
A groundbreaking development platform that serves as the foundation for remarkable solutions has been presented to the world in 2023, enabling all business cases in the smart home and building verticals. From single products to services, any manufacturer or developer can find the necessary resources to create unique solutions.
Discover how the KNX Ecosystem works by hovering over the different elements in the image below.
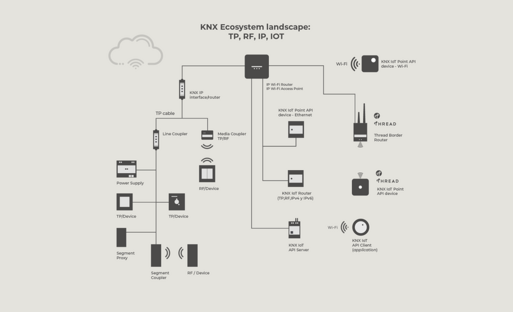
A Wi-Fi Access Point is a topology element required by the Wi-Fi network. It allows Wi-Fi-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Wi-Fi device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Wi-Fi as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IP Interface connects KNX TP-based installations with IP (IPv4) using the KNXnet/IP protocol. It offers tunneling connections, which are used by clients to establish a connection with the downstream KNX installation. KNX IP Routers provide interface functionality as well as routing capabilities. A KNX IP Router can link several KNX TP sections using IP as a backbone.
A Thread Border Router is a topology element required by the Thread network. Similar to a Wi-Fi access point, it allows Thread-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Ethernet device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Ethernet as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Thread device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Thread as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Router is a gateway between KNX TP, RF or IPv4 devices and KNX IoT devices. It can be a stand-alone device, but it can also be integrated into other network elements (e.g., Thread Border Router + KNX IoT Router).
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A Line Coupler is a topology element that connects a TP line with other TP lines via a TP backbone. A maximum of 15 lines can be coupled together, forming an area. Up to 15 areas can be coupled together using an Area Coupler.
A KNX Power Supply is required to power the twisted pair (TP) cable that connects KNX TP devices.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
A Segment Proxy enables KNX Data Secure communication with plain KNX communication. This can help prevent easily accessible KNX TP Secure devices (e.g., thermostats) from communicating with back-end KNX TP devices that are not secure. The communication up to the Segment Proxy will be secure.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
A Wi-Fi Access Point is a topology element required by the Wi-Fi network. It allows Wi-Fi-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Wi-Fi device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Wi-Fi as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IP Interface connects KNX TP-based installations with IP (IPv4) using the KNXnet/IP protocol. It offers tunneling connections, which are used by clients to establish a connection with the downstream KNX installation. KNX IP Routers provide interface functionality as well as routing capabilities. A KNX IP Router can link several KNX TP sections using IP as a backbone.
A Thread Border Router is a topology element required by the Thread network. Similar to a Wi-Fi access point, it allows Thread-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Ethernet device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Ethernet as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Thread device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Thread as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Router is a gateway between KNX TP, RF or IPv4 devices and KNX IoT devices. It can be a stand-alone device, but it can also be integrated into other network elements (e.g., Thread Border Router + KNX IoT Router).
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A Line Coupler is a topology element that connects a TP line with other TP lines via a TP backbone. A maximum of 15 lines can be coupled together, forming an area. Up to 15 areas can be coupled together using an Area Coupler.
A KNX Power Supply is required to power the twisted pair (TP) cable that connects KNX TP devices.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
A Segment Proxy enables KNX Data Secure communication with plain KNX communication. This can help prevent easily accessible KNX TP Secure devices (e.g., thermostats) from communicating with back-end KNX TP devices that are not secure. The communication up to the Segment Proxy will be secure.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
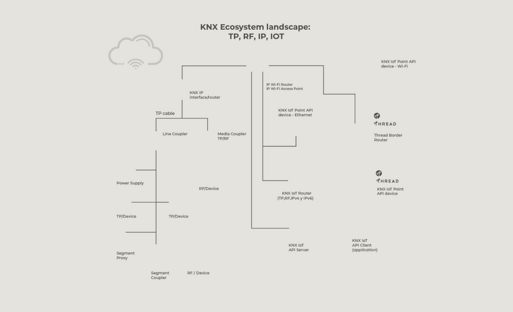

A Wi-Fi Access Point is a topology element required by the Wi-Fi network. It allows Wi-Fi-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.

A KNX IoT Point API device - Wi-Fi device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Wi-Fi as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.

A KNX IP Interface connects KNX TP-based installations with IP (IPv4) using the KNXnet/IP protocol. It offers tunneling connections, which are used by clients to establish a connection with the downstream KNX installation. KNX IP Routers provide interface functionality as well as routing capabilities. A KNX IP Router can link several KNX TP sections using IP as a backbone.

A Thread Border Router is a topology element required by the Thread network. Similar to a Wi-Fi access point, it allows Thread-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.

A KNX IoT Point API device - Ethernet device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Ethernet as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.

A KNX IoT Point API device - Thread device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Thread as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.

A KNX IoT Router is a gateway between KNX TP, RF or IPv4 devices and KNX IoT devices. It can be a stand-alone device, but it can also be integrated into other network elements (e.g., Thread Border Router + KNX IoT Router).

The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.

The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.

A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.

A Line Coupler is a topology element that connects a TP line with other TP lines via a TP backbone. A maximum of 15 lines can be coupled together, forming an area. Up to 15 areas can be coupled together using an Area Coupler.
A KNX Power Supply is required to power the twisted pair (TP) cable that connects KNX TP devices.

A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium

A Segment Proxy enables KNX Data Secure communication with plain KNX communication. This can help prevent easily accessible KNX TP Secure devices (e.g., thermostats) from communicating with back-end KNX TP devices that are not secure. The communication up to the Segment Proxy will be secure.

A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).

A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.

A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
A Wi-Fi Access Point is a topology element required by the Wi-Fi network. It allows Wi-Fi-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Wi-Fi device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Wi-Fi as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IP Interface connects KNX TP-based installations with IP (IPv4) using the KNXnet/IP protocol. It offers tunneling connections, which are used by clients to establish a connection with the downstream KNX installation. KNX IP Routers provide interface functionality as well as routing capabilities. A KNX IP Router can link several KNX TP sections using IP as a backbone.
A Thread Border Router is a topology element required by the Thread network. Similar to a Wi-Fi access point, it allows Thread-based devices to communicate with the LAN and WAN.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Ethernet device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Ethernet as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Point API device - Thread device is a certified device (Stack, Application) that uses Thread as its communication medium. Unlike KNX TP and KNX RF devices, the physical layer is not part of the KNX Specifications; instead, an IPv6-based communication medium is used.
A KNX IoT Router is a gateway between KNX TP, RF or IPv4 devices and KNX IoT devices. It can be a stand-alone device, but it can also be integrated into other network elements (e.g., Thread Border Router + KNX IoT Router).
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
The KNX IoT API Server uses the KNX Information Model, natively exported by ETS6, to expose a standardized API for third parties to communicate with KNX installations. A certified KNX IoT API Server has been tested against KNX specifications and is compliant with the standard API model. Third parties can develop clients that seamlessly work with KNX IoT API Servers, regardless of the manufacturer.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A Line Coupler is a topology element that connects a TP line with other TP lines via a TP backbone. A maximum of 15 lines can be coupled together, forming an area. Up to 15 areas can be coupled together using an Area Coupler.
A KNX Power Supply is required to power the twisted pair (TP) cable that connects KNX TP devices.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
A Segment Proxy enables KNX Data Secure communication with plain KNX communication. This can help prevent easily accessible KNX TP Secure devices (e.g., thermostats) from communicating with back-end KNX TP devices that are not secure. The communication up to the Segment Proxy will be secure.
A TP/RF media coupler connects an RF segment with a TP line. It can be added as another 'line' or can extend an existing TP line with an RF sub-segment (in this case it is called Segment Coupler).
A KNX RF device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a RF physical layer (RF) as its communication medium.
A KNX TP device is a certified device (Physical Layer, Stack, Application) that uses a twisted pair cable (TP) as its communication medium
KNX IoT Development and KNX Startup Incubator
Interested in KNX IoT Development? Discover more on KNX IoT and how you can develop for KNX IoT, the benefits and the supprt KNX offers via our KNX Startup Incubator.
Join us on our journey
Create a MyKNX account to stay updated on the latest in KNX IoT, technology events, innovative KNX products and more. Join our community to access exclusive insights and be part of the future of sustainable energy. Sign up today and stay connected!
